افضل دكتور عظامProximal Humeral Fractures, Extra Aarticular 2-Part Subgroup Important Considerations
Extra Articular 2-Part, Greater Tuberosity, Non Displaced
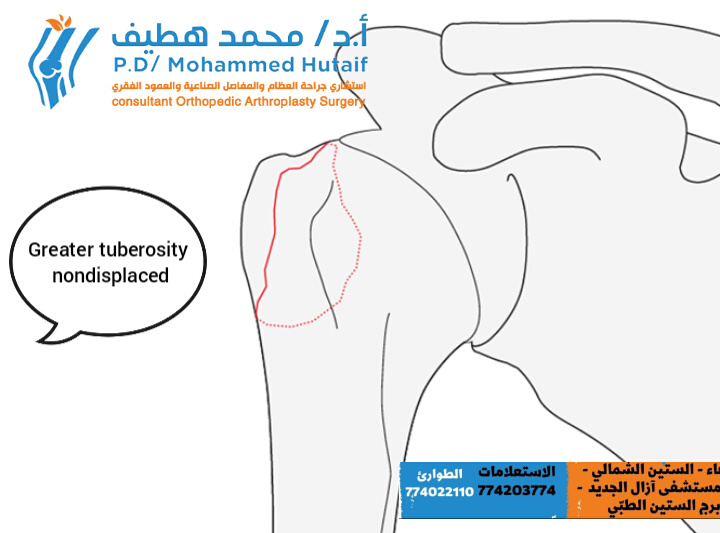
This fracture subgroup consists of fractures of the greater tuberosity which are truly not displaced. They heal typically very well under conservative treatment and do not tend to displace during the healing period.
These fractures are unifocal extraarticular proximal humerus fractures involving the greater tuberosity. The greater tuberosity is the attachment of supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendons and its integrity is important for proper shoulder function. Proximal displacement, even as little as 5 mm, of a fracture of the greater tuberosity compromise shoulder abduction. This is due to tuberosity impingement on the coracoacromial arch and/or shortening of the involved rotator cuff tendons.

This fracture subgroup consists of fractures of the greater tuberosity which are superiorly and/or posteriorly displaced.
The typical displacement of the greater tuberosity is posterosuperiorly.
A displacement more than 5 mm is usually considered significant and should be treated surgically.
These fractures are unifocal extraarticular proximal humerus fractures involving the greater tuberosity. The greater tuberosity is the attachment of supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendons and its integrity is important for proper shoulder function. Proximal displacement, even as little as 5 mm, of a fracture of the greater tuberosity compromise shoulder abduction. This is due to tuberosity impingement on the coracoacromial arch and/or shortening of the involved rotator cuff tendons.

General considerations
Fracture without frontal malalignment
Fracture with varus malalignment


