Anterior Cruciate Ligament injuries SYMPTOMS
When the ACL is injured, you may hear a "pop" noise and you may feel your knee is bursting from under you. Other typical symptoms include:
- A loud noise or a "pop" sensation in the knee.
- Severe pain and inability to continue activity
- Pain with rapid swelling. Within 24 hours, your knee will be swollen. If ignored, the swelling and pain may go away on its own. However, if you try to return to exercise, your knee is likely to be unstable and will cause further damage to the lining (meniscus) in your knee.
- Loss of full range of motion
- Discomfort while walking to the top
- Feeling unsteady or "lax" with weight bearing
Seek immediate care if any injury to your knee causes signs or symptoms of an ACL injury. The knee joint is a complex structure of bones, ligaments, tendons and other tissues that work together. It is important to get a prompt and accurate diagnosis to determine the severity of the infection and to get the appropriate treatment.
Appropriate training and exercises can help reduce the risk of an ACL injury. A sports medicine doctor, physical therapist, sports coach or other sports medicine professional can provide evaluation, instructions and feedback that can help you reduce your risk.
During a physical exam, your doctor will check your knee for swelling and pain - comparing your injured knee to your uninjured knee. He or she may also move your knee in a variety of positions to assess the range of motion and general function of the joint. The doctor often performs a Lachman test to see if the ACL is healthy.
If the ACL is torn, the examiner will feel the increased forward movement (up or forward) of the tibia relative to the femur (especially when compared to a normal leg)
In addition to conducting special tests to determine the meniscus tear and injury to other knee ligaments,
Diagnosis can often be made based on a physical exam alone, but you may need tests to rule out other causes and determine the severity of the injury.
These tests may include:
X ray .
X-rays may be needed to rule out a broken bone. However, X-rays do not show soft tissues, such as ligaments and tendons.
Magnetic resonance imaging.
An MRI uses radio waves and a strong magnetic field to create images of the hard and soft tissues in your body. An MRI can show the extent of the ACL and signs of damage to other tissues in the knee, including cartilage.
Ultrasound.
Using sound waves to visualize internal structures, ultrasound can be used to check for injuries to the ligaments, tendons, and knee muscles.
Quick first aid care can reduce pain and swelling once your knee is injured.
Once the injury occurs, follow the self-care model at home:
- General rest is essential to recovery and limits weight bearing on your knee.
- Try putting ice on your knee at least every two hours for 20 minutes each time.
- Wrap an elastic bandage or a compressive wrap around your knee.
Non-surgical treatment
A torn ACL will not heal without surgery. But non-surgical treatment may be effective for patients who are elderly or have a very low activity level. If the knee's overall stability is intact, your doctor may recommend simple, non-surgical options.
Your doctor may recommend a brace to protect your knee from instability.
To further protect your knee, you may be given crutches to prevent you from putting too much weight on your leg.
surgical treatment
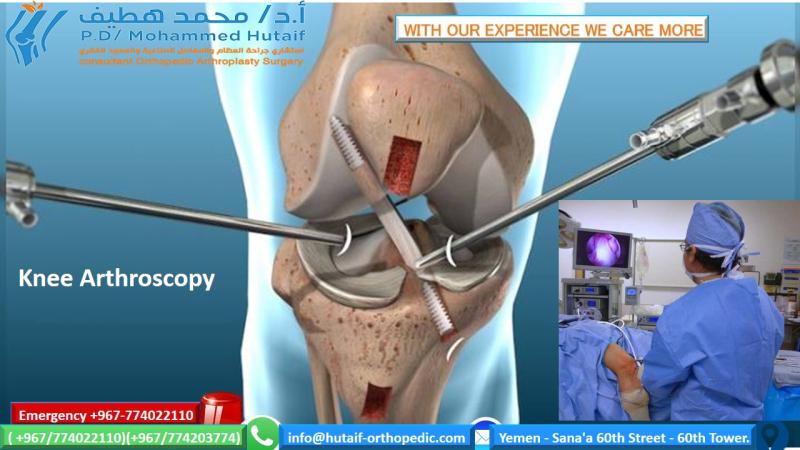
Ligament reconstruction. Most ACL tears cannot be stitched together. To surgically repair the ACL and restore stability to the knee, the ligament must be reconstructed. Your doctor will replace your torn ligament with a tissue graft.
Grafts can be obtained from several sources. It is most often taken from the patellar tendon, which runs between the kneecap and the shin bone. The hamstrings at the back of the thigh are a common source of grafts. Sometimes the quadriceps tendon, which runs from the knee to the thigh, is used.
Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery is performed using an arthroscopy using small incisions. arthroscopy surgery is less invasive.
Benefits of less invasive techniques include less pain than surgery, less time spent in the hospital, and faster recovery times
Whether your treatment includes surgery or not, rehabilitation plays a vital role in getting you back to your daily activities. A physical therapy program will help you restore knee strength and mobility.
If you undergo surgery, physical therapy first focuses on returning movement to the joint and surrounding muscles. This is followed by a strengthening program designed to protect the new ligament. This strengthening gradually increases pressure across the ligament
Next page:How do you tell if ACL is torn or sprained?


